Incontinence in literal means involuntary leakage of urine. The incontinence may be urge incontinence or leakage following inability to postpone urination. It may be stress Incontinence which is leakage on cough or stress.
Million of men and women suffer from incontinence in silence thinking that it is an inevitable outcome after multiple child births or ageing.
The men also have prostate which can equally be responsible for the incontinence.
Types of Incontinence
Stress Urinary Incontinence ( SUI)
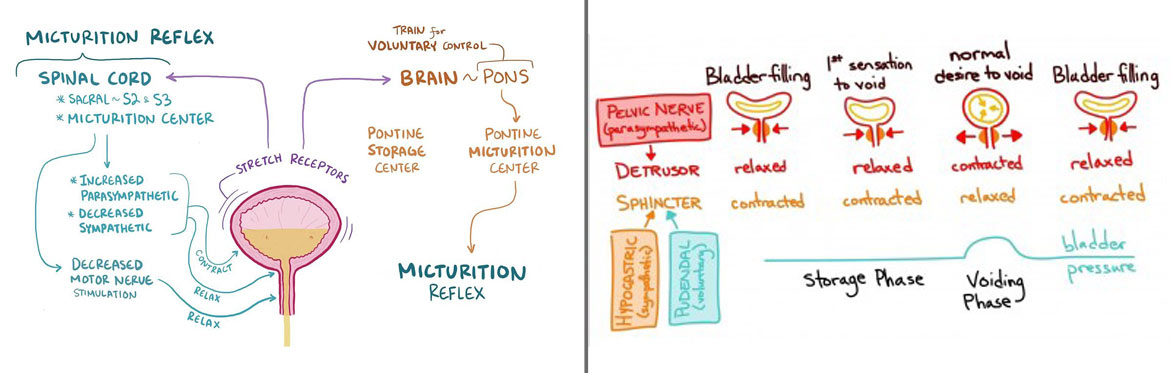
This type of incontinence occurs when the control valve of the bladder outlet is damaged or weakened because of multiple causes. This may include pelvic prolapse, multiple child births, previous surgery usually prostatectomies in men. This leads to leakage of urine on any involuntary abdominal stress for example coughing or sneezing or straining.
Urgency Incontinence
This type of leakage occurs when the incontinence happens when one is unable to postpone urination. This occurs due to over activity of bladder or uninhibition of bladder contractility. This may be de novo or on its own or may be the result of any previous surgery or procedure.
Mixed Incontinence
When both stress and urgency incontinence occur together.
Overflow Incontinence
This occurs when leakage occurs after inability to pass out urine completely, leading to spillover of urine outside leading to wetting of clothes.
Treatment Available
The patients are often not forthcoming due to embarrassment and taking it as normal part of ageing. The treatment is usually directed by the cause of incontinence and mostly starts from the basic therapy like medical treatment with drugs.
Evaluation
Includes Bladder Diary which is basically a record of the fluid that one consumes vis a vis the urine collection charted over couple of days which is an indirect measure of urine output, toilet habits and hydration of the patient.
Along with these basic tests are included Ultrasonography of the abdomen which test the kidneys and bladder and the post void residual urine.
General Urine tests include Urine routine and Culture.
Uroflowetry : A measure of how fast or slow the speed of exiting urine is, which when scaled against population database provides the appropriate measure of obstruction.
Urodynamics : It is an elaborate measure of pressure of the bladder measured against the flow and symptoms of the patient. This is never a first line treatment and is indicated only in rare circumstances when the treatment has failed or rare causes are suspected as in Neurological causes.
Treatment is started with correction of lifestyle if indicated to drugs and last resort any corrective surgery.
This may include Prostatectomy in Male.
FAQ’s
- What is incontinence?
Incontinence refers to the involuntary loss of urine or feces, often associated with a loss of bladder or bowel control. It can range from occasional leaks to a complete inability to control the bladder or bowel.
- Who can suffer from incontinence?
Incontinence can affect people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. While it’s more common in older adults, it’s not an inevitable part of aging. Various factors, including medical conditions, childbirth, and lifestyle, can contribute to incontinence.
- What are the types of incontinence?
Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI): Involuntary leakage of urine during activities that increase abdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or exercising.
- Urgency Incontinence: Also known as overactive bladder, it involves a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by involuntary leakage.
- Overflow Incontinence: Occurs when the bladder doesn’t empty completely, leading to frequent or constant dribbling of urine.
- What causes Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI)?
SUI is often caused by weakened pelvic floor muscles, commonly due to childbirth, obesity, or pelvic surgery. It can also result from conditions that increase abdominal pressure.
- What is Urgency Incontinence?
Urgency incontinence is characterized by a strong, often uncontrollable, urge to urinate. It can be caused by bladder muscle overactivity, neurological issues, or urinary tract infections.
- Can both stress and urgency incontinence occur together?
Yes, individuals may experience a combination of stress and urgency incontinence, a condition known as mixed incontinence. This can present additional challenges in management.
- What is Overflow Incontinence?
Overflow incontinence occurs when the bladder doesn’t empty properly, leading to constant dribbling. It can result from an obstruction, nerve damage, or weak bladder muscles.
- Why do people hesitate to seek treatment for incontinence?
Stigma, embarrassment, or the misconception that incontinence is a normal part of aging often lead people to avoid seeking help. However, effective treatments are available, and healthcare professionals are trained to address these concerns with sensitivity.
- What is the first step in evaluating incontinence?
A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional is crucial. This may include a medical history review, physical examination, urinalysis, and, in some cases, advanced tests such as urodynamic studies.
- What lifestyle changes can help manage incontinence?
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Strengthening pelvic floor muscles through exercises known as Kegels.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the bladder.
- Fluid Management: Adjusting fluid intake, especially before bedtime, can minimize symptoms.
- Bladder Training: Gradually increasing the time between bathroom visits to improve bladder control.
Effective management of incontinence often involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, behavioral strategies, and, if necessary, medical interventions. Seeking professional guidance can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals experiencing incontinence.


